TL;DR#
Stow is a tool for managing configurations across different programs in your system.
Stow#
Stow is a symlink farm manager designed to manage distinct sets of software configurations by leveraging symbolic links.
How It Works#
- Symbolic Links: Stow creates symbolic links for configuration files.
- Main Folder: Create a main folder to store your dotfiles. Each configuration should reside in a separate subdirectory.
- Maintain Folder Structure: The folder structure inside the main folder must match the actual location of the configuration files.
- Use Stow: Utilize Stow to create and manage symbolic links efficiently.
Usage#
Installation#
To install Stow, use the following commands based on your system:
Debian based (Debian, Ubuntu, … etc)
sudo apt install stowRHEL based (RedHat, Fedora, … etc)
sudo dnf install stow
Using Stow#
Read the Manual.
Learn more about Stow by reading the manual:
man stow
Create a directory for storing your dotfiles.
For example, name it mydotfiles.
mkdir mydotfiles
Create Subdirectories for Configurations.
Each configuration file or folder should have its own subdirectory. The folder structure within mydotfiles must match the actual locations of the files.
For example:
For a .gitconfig file (located in ~), create a git folder.
For fastfetch (located in ~/.config/fastfetch), create fastfetch/.config folder.create a nested structure:
cd mydotfiles mkdir git mkdir -p fastfetch/.config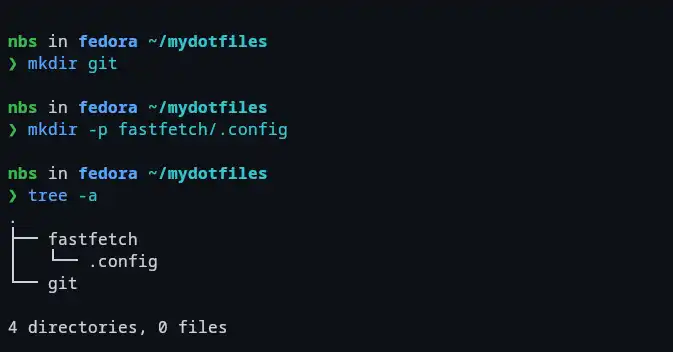
Move Configuration Files into mydotfiles.
Transfer the configuration files to their respective subdirectories:
mv ~/.gitconfig mydotfiles/git #git mv ~/.config/fastfetch mydotfiles/fastfetch/.config/ #fastfetch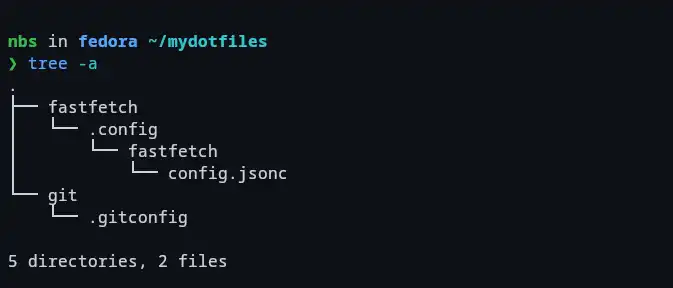
Use Stow to Create Symbolic Links.
Run Stow to generate symbolic links in their original locations:
stow git stow fastfetch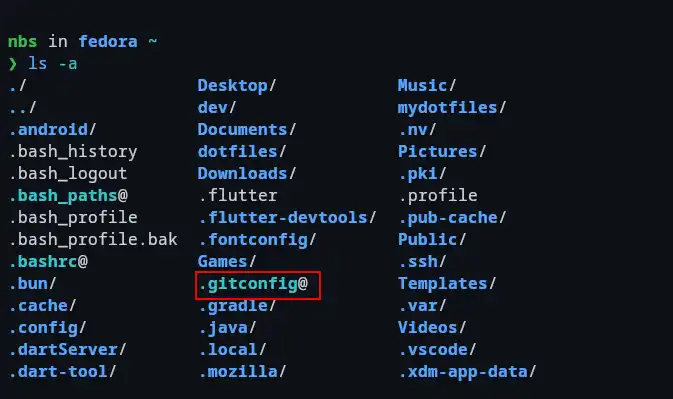
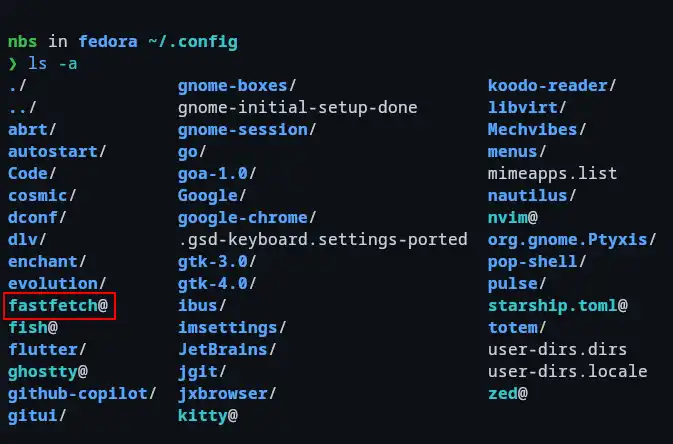
The symbolic links are created, and they can be identified by an @ symbol (e.g., .gitconfig@) in some shells like Fish.
Removing Symbolic Links#
If you want to remove symbolic links without deleting the original dotfiles, use the -D option:
cd mydotfiles
stow -D gitExample: My Dotfiles#
Here’s an example of a dotfiles repository managed with Stow:
